Look-Alike Sound-Alike (LASA) medications include medications that are visually the same in physical appearance or packaging and names of medications that have similar spelling or similar phonetics.
As more medicines and new brands are being marketed in addition to the thousands already available, many of these medication names may look or sound alike. Confusing medication names and similar product packaging may lead to potentially harmful medication errors. The increasing potential for LASA medication errors was also highlighted in the Joint Commission’s Sentinel Event Alert.
Emphasis on patient safety in the naming of medicines is now undertaken by national and international regulatory and advisory boards. The World Health Organisation’s International Non-proprietary Names Expert Group works to develop international non-proprietary names for pharmaceutical medicinal substances for acceptance
worldwide.
Healthcare organizations need to institute risk management strategies to minimize adverse events with LASA medications and enhance patient safety. To aid in this effort, this article on Handling of Look-Alike Sound-Alike Medications is published, it is hoped that errors relating to LASA medications can be minimized, if not eliminated, through identification and implementation of safety precautions.
Common Risk Factors
Common risk factors associated with LASA medications include:
- Illegible handwriting
- Incomplete knowledge of drug names
- Newly available products
- Same packaging or labeling
- Similar strengths, dosage forms, frequency of administration
- Similar clinical use
Strategies To Avoid Errors
- Procurement
- Storage
- Prescribing
- Dispensing/Supply
- Administration
- Patient Education
1. Procurement
(a) Minimize the availability of multiple medicine’s strengths.
(b) Whenever possible, avoid the purchase of medicines with similar packaging and appearance. As new products or packages are introduced, compare them with existing packaging.
2. Storage
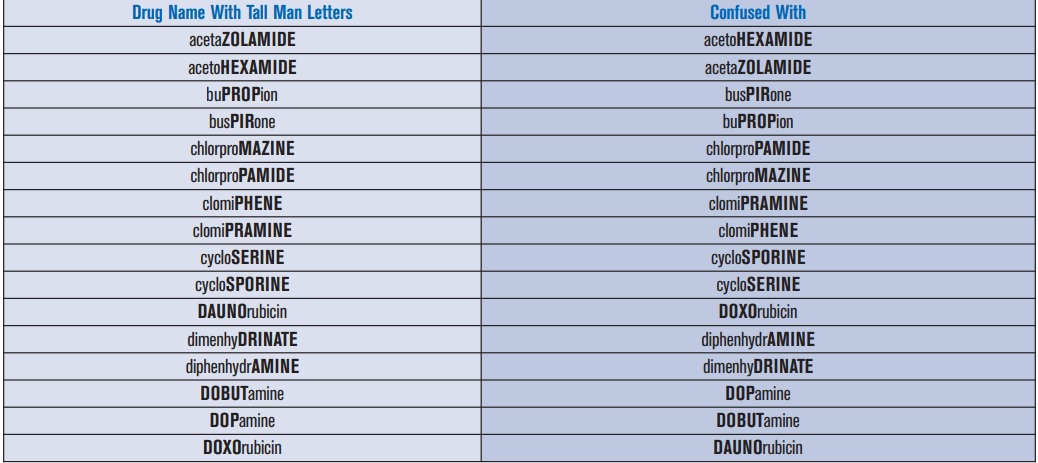
(a) Use Tall Man lettering to emphasize differences in medications with sound-alike names.
Tall Man lettering (or Tallman lettering) is the practice of writing part of a medicine name in upper case letters to help distinguish soundalike, look-alike medications from one another to avoid medication errors.
Tall Man lettering involves highlighting the dissimilar letters in two names to aid in distinguishing between the two. The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP), U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA), The Joint Commission and other safety-conscious organizations have promoted the use of Tall Man lettering as one means of reducing confusion between similar medication names.
Examples of Tall Man lettering are metFORMIN and metoPROLOL.
(b) Use additional warning labels for look-alike medicines. Warning labels should be uniform throughout the respective facility to facilitate identification.
3. Prescribing
(a) Write legibly. Write clearly whether on an inpatient order or on a prescription.
(b) The prescription should clearly specify the name of the medication, dosage form, dose and complete direction for use.
(c) Include the diagnosis or medication’s indication for use. This information helps to differentiate possible choices in illegible orders.
(d) Whenever possible, drug names in computerized prescriber order entry (CPOE) should incorporate Tall Man lettering.
(e) Communicate clearly. Take your time in pronouncing the drug name whenever an oral order has to be made. Ask that the recipient of the oral communication repeat the medication name and dose. Verbal orders should be limited to emergency situations only.
4. Dispensing
(a) Identify medicines based on their name and strength and not by its appearance or location.
(b) Check the appropriateness of the dose for the medicines dispensed.
(c) READ medication labels carefully at all dispensing stages and perform a triangle check. Triangle check is to check actual medicines against the medicines’ labels and against the prescription.
(d) Double-checking should be conducted during the dispensing and supply process.
(e) Highlight changes in medication appearances to patients upon dispensing.
5. Administration
Read medication labels carefully during the administration process and perform a triangle check. Triangle check is to check medicine against the medication label and against the prescription.
6. Patient Education
(a) Inform patients on changes in medication appearances.
(b) Educate patients and their caregivers to alert healthcare providers whenever a medication appears to vary from what is usually taken or administered.
(c) Encourage patients and their caregivers to learn the names of their medications.
Table 1. FDA-Approved List of Generic Drug Names with Tall Man Letters