The Ultimate Guide for Learners and Buyers
Are you planning to buy a UV Vis Spectro photometer? We know that buying a UV Vis Spectro Photometer can be a tough job especially when you do not have expertise in it. Interesting thing is that – you are not alone. After helping 1000+ customers buy the right UV Vis Spectro Photometer, we have planned to make the most detailed guide on how to buy a UV Vis Spectro photometer without having technical knowledge.
The guide is easy to read and follow whether you are in your early 20’s or 50+ age. Anyhow, if you still need our help in selecting the right model of Spectrophotometer, our technical team is available 24/7 for your help free.
Which things did you need to know before buying a Spectrophotometer?
- A brief knowledge about UV Vis Spectro Photometer and its applications
- Your careful attention for 15 minutes to read this guide.
Yes, only 15 minutes you need to understand, how to buy UV Vis Spectro Photometer and you will pass through the whole steps.
In this guide, you will cover.
Chapter 1: Spectrophotometer Overview
Chapter 2: Working principle of Spectrophotometer
Chapter 3: Types of Spectrophotometer
Chapter 4: Main parts of Spectrophotometer
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting of common problems, which occur during operation
Chapter 6: Spectrophotometer applications
Chapter 7: Merits and demerits of HPLC
Chapter 8: Famous brands of HPLC
If you want to Learn HPLC then please read the article
Learn HPLC: The Ultimate Guide for Learners & Buyers
Chapter 1
Spectrophotometer Overview
Ultraviolet-visible (UV Vis) spectrophotometry is a quantitative technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. When the incident light strikes on the matter it can either be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. The atomic excitation occurs due to the absorbance of radiations in UV Vis range, which refers to the transition of molecules from the ground state to an excited state. Before an atom can change excitation states, it must absorb sufficient radiation for electrons to move into higher molecular orbits. If there is a Shorter bandgap between electrons then there will be the absorption of shorter wavelengths of light. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light transmitted through a sample compared to a reference measurement of the incident light source.
The amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the concentration of the sample and the distance the light travels through the sample. Therefore, UV-Vis spectrophotometers are able to determine the concentration of specific analytes in a microvolume by controlling the Wavelengths and path length.
Chapter 2
Working principle of Spectrophotometer
The working principle of the Spectrophotometer is based upon Beer-Lambert’s law, this law stated as the amount of light absorbed by a color solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution and the path length.
Mathematically,
A ∝ cl
Where,
A = Absorbance / Optical density of solution
c = Concentration of solution
l = Path length
or, A = ∈cl
∈ = Absorption coefficient
Chapter 3
Types of UV Vis Spectro photometer
TYPES OF SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Following are the two different types of spectrometer
- Single beam spectrophotometer
- Double beam spectrophotometer
Single Beam Spectrophotometer:
This type of spectrophotometer works between 325 nm to 1000nm wavelength using a single beam of light. Light travels in uni-direction and read the blank and test solution same.
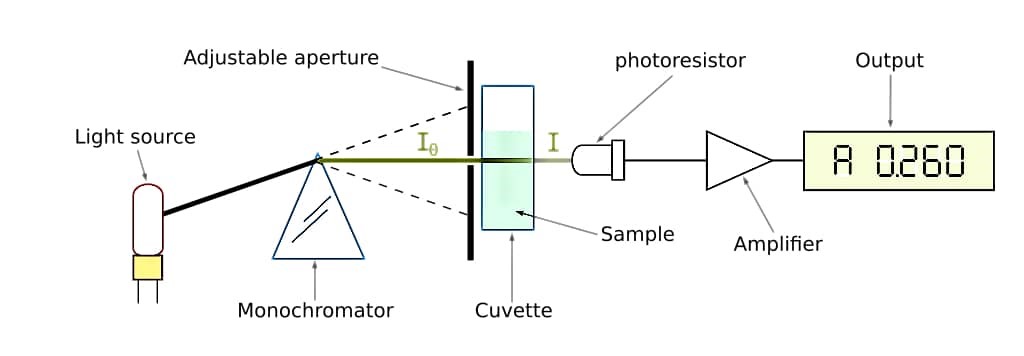
Double Beam Spectrophotometer:
This type of spectrophotometer works between 185 nm to 1000 nm wavelength. This instrument splits the light from the Monochromator into two beams. One beam is used for reference and the other for sample reading. It eliminates the error which occurs due to fluctuations in the light output and the sensitivity of the detector.
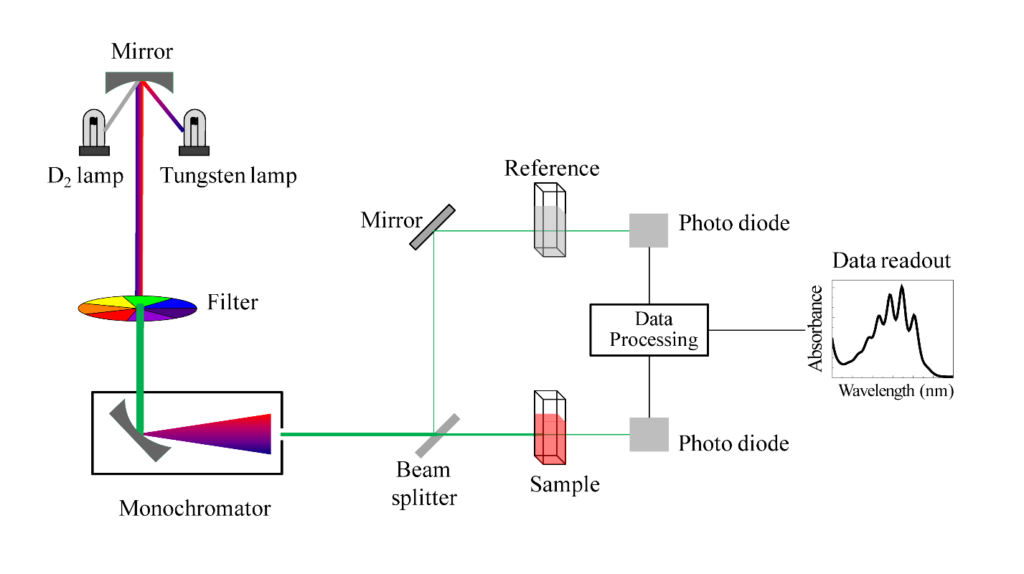
Chapter 4
Main parts of UV Vis Spectro photometer
MAIN PARTS OF SPECTROPHOTOMETER
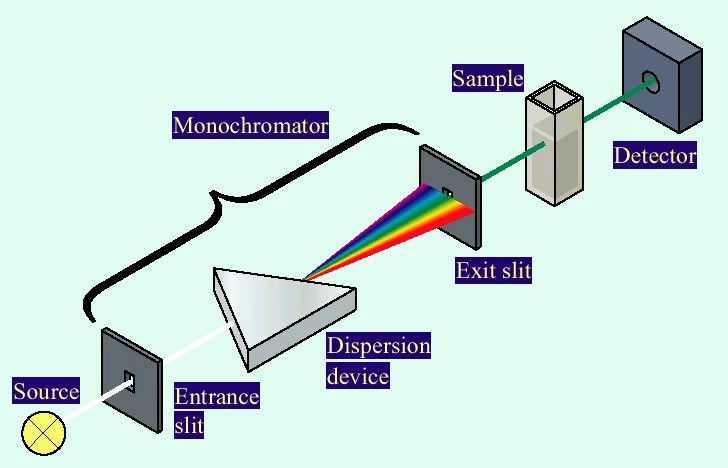
There are following Seven different parts of spectrophotometer
Light source:
In spectrophotometer different sources of light are used to produce light of different wavelengths. Tungsten lamps common source of light used in the spectrophotometer for the visible spectrum. Hydrogen lamp and the deuterium lamp for Ultraviolet radiation. Nernst filament or globaris is the most satisfactory source of IR radiation.
Monochromator:
The main function of a monochromator is to separate the color components of light. To select the particular wavelength, prism or diffraction grating is used to split the light from the light source
Sample holder:
Test tubes or Cuvettes are used to hold the colored solutions. They are made up of glass at a visible wavelength.
Beam splitter:
It is present only in a double beam spectrophotometer. It is used to split the single beam of light coming from the light source into two beams.
Mirror:
It is also present only in a double beam spectrophotometer. It is used in the right direction to the split light from the beam splitter.
Photodetector system:
When light falls on the detector system, an electric current is generated that reflects the galvanometer reading.
Measuring device:
The current from the detector is fed to the galvanometer. The reading on the meter is directly proportional to the intensity of light.
Chapter 5
Troubleshooting of common problems, which occur during operation
Problem 1: When the instrument scans the sample, a straight line is displayed
Possible cause: The software is malfunctioning.
Solution: Exit the operating system, restart the computer, and scan again.
Problem 2: After the UV/Visible spectrophotometer is turned on, the light source is not bright
possible reason:
①The light source bulb is damaged;
②The fuse is burned out.
Solution: replace the deuterium lamp or tungsten lamp; replace the fuse.
Problem 3: The instrument noise is relatively large
Possible cause: The light source bulb has been used for longer than its life span.
Solution: Replace the light source bulb.
Problem 4: A certain section of the baseline is particularly noisy
Possible cause: The corresponding filter in the wavelength range is damp and moldy, which seriously loses light energy.
Remedy: Replace the corresponding filter.
Problem 5: A communication error is prompted during the self-test of the instrument
Possible cause: The data cable between the instrument and the computer is not connected properly.
Chapter 6
Spectrophotometer’s applications
Detection of Impurities
UV-VIS spectroscopy is one of the best methods for the determination of impurities in organic molecules. Additional peaks can be observed due to impurities in the sample and it can be compared with that of standard raw material. The impurities can be detected by measuring the absorbance at a specific wavelength.
Benzene can be detected by its absorption at 255 nm.
Structure elucidation of organic compounds
UV-VIS spectroscopy is useful in the structure elucidation of organic molecules, the presence or absence of unsaturation, the presence of hetero atoms.
From the location of peaks and combination of peaks, it can be concluded that whether the compound is saturated or unsaturated, hetero atoms are present or not, etc.
Quantitative analysis
UV-VIS spectroscopy can be used for the quantitative determination of compounds that absorb UV radiation. This determination is based on Beer’s law which is as follows.
A = log I0 / It = log 1/ T = – log T = abc = εbc
Where ε is extinction coefficient, c is concentration, and b is the length of the cell that is used in UV-Vis Spectrophotometer.
Qualitative analysis
UV-VIS spectroscopy can characterize those types of compounds that absorb UV radiation. Identification is done by comparing the absorption spectrum with the spectra of known compounds.
UV absorption spectroscopy is generally used for characterizing aromatic compounds and aromatic olefins.
Dissociation constants of acids and bases
PH = PKa + log [A–] / [HA]
From the above equation, the PKa value can be calculated if the ratio of [A–] / [HA] is known at a particular PH and the ratio of [A–] / [HA] can be determined spectrophotometrically from the graph plotted between absorbance and wavelength at different PH values.
Chemical kinetics
Kinetics of reaction can also be studied using UV spectroscopy. The UV radiation is passed through the reaction cell and the absorbance changes can be observed.
Quantitative analysis of pharmaceutical substances
The essay of many drugs can be calculated by making a suitable solution of the drug and measuring the absorbance at a specific wavelength.
Diazepam tablets can be analyzed by 0.5% H2SO4 in methanol at the wavelength 284 nm.
Molecular weight determination
Molecular weights of compounds can be measured spectrophotometrically by preparing the suitable derivatives of these compounds.
For example, if we want to determine the molecular weight of amine then it is converted into amine picrate. A then known concentration of amine picrate is dissolved in a liter of solution and its optical density is measured at λmax 380 nm. After this, the concentration of the solution in gm moles per liter can be calculated by using the following formula.
“c” can be calculated using the above equation, the weight “w” of amine picrate is known. From “c” and “w”, the molecular weight of amine picrate can be calculated. And the molecular weight of picrate can be calculated using the molecular weight of amine picrate.
As HPLC detector
A UV-Vis spectrophotometer may be used as a detector for HPLC. The presence of an analyte gives a response that can be assumed to be proportional to the concentration. For more accurate results, the instrument’s response to the analyte in the unknown should be compared with the response to a standard; as in the case of the calibration curve.
Chapter 7
Merits and Demerits of HPLC
Advantages of UV Visible Spectroscopy:
- The main advantage of the UV-VIS spectrophotometer is the accuracy
- The UV-VIS spectrometer is easy to handling and use
- The UV-VIS spectroscopy is simple to operate
- It is cost effective instrument
- Cover the entire of ultraviolet and visible
- It can be utilized in the qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- The Derivative graph can be obtained by UV-VIS spectrophotometer.
- It can be used in the degradation study of drug.
Disadvantages of UV Visible Spectroscopy:
- It can be analyzed only those molecules which have chromophores.
- The results of the absorption can be affected by pH, temperature, contaminants, and impurities.
- Only liquid samples are possible to analyze
- It takes time to get ready to use it
- Cuvette handling can affect the reading of the sample.
Chapter 8
Famous brands of HPLC
Some famous brands of UV-VIS spectrophotometer


