Total Microbial Count test refers to the counting of viable microorganisms in any dosage form or raw material etc. There are several official methods for conducting the total microbial count test. I will give you a step-by-step guide on performing the total microbial count test in this article.
Having a structured checklist can be invaluable to ensure you conduct the Total Microbial Count test effectively and meet all necessary standards. Our Total Microbial Count Testing Checklist provides a detailed guide on required materials, step-by-step procedures, and essential tips to streamline your process. Download it now to simplify your testing workflow and enhance accuracy!
Need Step by Step Checklist?
Download our free Total Microbial Count Check List
Now let us talk about the procedure of conducting this test. There are two official tests for conducting total microbial tests which I think are easy to perform and are cost-effective.
- Pour Plate Method
- Spread Plate Method
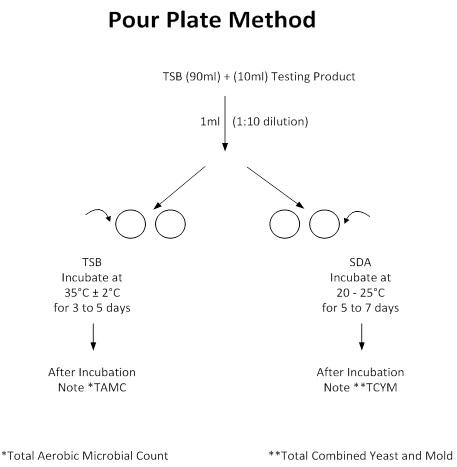
Pour Plate Method
Here’s how to get started with the Pour Plate Method:

- Prepare Your Culture Media: Follow the supplier’s instructions to prepare Tryptic Soy Agar, Tryptic Soy Broth, and Sabouraud Dextrose Agar. Don’t forget to autoclave them for sterilization.
- Sample Preparation: Take your sample:
- For solid dosage forms (tablets, capsules, or powder), weigh 10 grams.
- For liquid dosage forms (syrups or suspensions), measure 10 ml. Suspend or dissolve the sample in 90 ml of sterilized Tryptic Soy Broth. Now you have a 100 ml solution.
- Inoculation: Aseptically take 1 ml of this solution and transfer it into two sterilized Petri plates. Incubate the remaining broth at 30-35 °C for 24-48 hours.
- Adding Agar: Pour 15-20 ml of molten Tryptic Soy Agar into the plates. Gently swirl for even mixing. For the remaining two plates, pour Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) instead.
- Incubation: Allow the agar to solidify, then:
- Incubate the TSA plates at 30-35 °C for 3-5 days.
- Incubate the SDA plates at 20-25 °C for 5-7 days.
And that’s it! You’re ready to observe the microbial colonies.
Spread Plate Method
The Spread Plate Method is another simple and effective option:
- Prepare Your Sample: Like before, weigh 10 grams of a solid sample or measure 10 ml of a liquid sample. Suspend it in 90 ml of sterilized Tryptic Soy Broth.
- Inoculation: Add 1 ml of this inoculated broth onto a TSA plate. Use a sterile glass spreader to evenly distribute the sample.
- Incubation: Incubate the plates:
- TSA plates at 30-35 °C for 3-5 days.
- SDA plates at 20-25 °C for 5-7 days.
After incubation, count the colonies. The results are expressed in colony-forming units (CFU). If no colonies are observed, report the result as fewer than 10 microorganisms per gram or milliliter.
Have additional questions?
We’re here to help. Let’s talk.
Documentation and Reporting of Results
Once the test is complete, it’s time to record your findings. Here’s how:
- Bacterial (Aerobic) Count: TAMC (Total Aerobic Microbial Count)
- Mold & Yeast Count: TCYM (Total Combined Yeast & Mold)
Record these counts on the microbiological testing report. Multiply the observed counts by a factor of 10 for final results. For instance, if no growth is observed, you can proudly declare: “Fewer than 10 microorganisms per gram/ml.”
Ensuring accurate microbiological testing is essential not only for dosage forms but also for packaging materials, as explained in our article on Microbiological Testing of Primary Packaging Material.
Acceptance Criteria for Microbiological Quality of Non-Sterile Dosage Forms
To ensure your results meet quality standards, refer to the acceptance criteria for various dosage forms:
|
Total Microbial Count |
Acceptance Criteria |
||
|
TAMC (cfu/g or cfu/ml) |
TCYM (cfu/g) |
Specified microorganisms |
|
|
Non-aqueous preparation for oral use |
103 |
102 |
Absence of E.coli in 1g or 1ml. |
|
Aqueous preparation for oral use |
102 |
101 |
Absence of E.coli in 1g or 1ml. |
|
Oromucosal use |
102 |
101 |
Absence of Staphylococcus aureus in 1g or 1ml Pseudomonas aeruginosa in 1g or 1ml. |
|
Vaginal use |
102 |
101 |
Absence of Candida albicans in 1g or 1ml Pseudomonas aeruginosa in 1g or 1ml Staphylococcus aureus in 1g or 1ml. |
By following these steps and maintaining proper documentation, you’re not only ensuring compliance but also contributing to the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Happy testing!



The procedure is well defined and helpful.Could you please let to know that how the empty primary packs be checked for microbiology (bottles and caps used to pack oral syrups) and what is the maximum allowed limit for TAMC and TYMC for empty bottles /packs used for oral syrups